
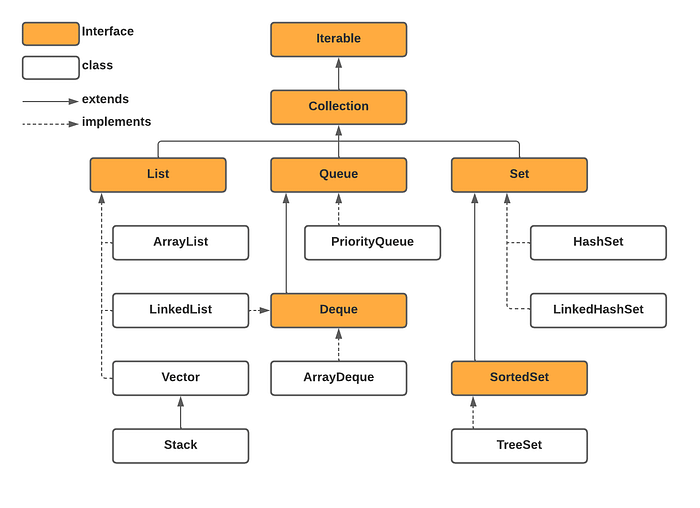
We will take a look into java.util.Set in this article. The Set is part of the collections framework in Java. It is an interface and it has three main concrete classes. Set doesn’t allow duplicates.
HashSet
It implements the Set interface. Internally, it’s based on HashMap. It doesn’t maintain insertion order and it doesn’t guarantee that the order will remain constant over time. It allows null value. HashSet is not synchronized. It offers constant time performance for the basic operations such as add, remove, contains, and size.
LinkedHashSet
This class extends the HashSet class and implements the Set interface. It maintains a doubly-linked list in addition to HashMap(hash table). The linked list defines the insertion order. So the main difference between LinkedHashSet and HashSet is that LinkedHashSet maintains the insertion(iteration) order. It allows null value. HashSet is not synchronized. It offers constant time performance for the basic operations such as add, remove, contains, and size.
TreeSet
A NavigableSet implementation based on a TreeMap. The elements are sorted using their natural ordering, or by a Comparator provided at a set creation time. It is not synchronized.
Let’s see one more example with our own sorting order.
In both examples, I didn’t create from the Set reference type but with TreeSet because otherwise, it loses it is NavigableSet methods.
Please take my Java Course for video lectures.This article is part of the series of articles to learn Java programming language from Tech Lead Academy:Introduction to programming
OS, File, and File System
Working with terminal
Welcome to Java Programming Language
Variables and Primitives in Java
Convert String to numeric data type
Input from the terminal in Java
Methods with Java
Java Math Operators and special operators
Conditional branching in Java
Switch statement in Java
Ternary operator in Java
Enum in Java
String class and its methods in Java
Loops in Java
Access modifiers in Java
Static keyword in Java
The final keyword in Java
Class and Object in Java
Object-Oriented Programming in Java
OOP: Encapsulation in Java
OOP: Inheritance in Java
OOP: Abstraction in Java
OOP: Polymorphism in Java
The method Overriding vs Overloading in Java
Array in Java
Data Structures with Java
Collection framework in Java
ArrayList in Java
Set in Java
Map in Java
Date and Time in Java
Exception in Java
How to work with files in Java
Design Patterns
Generics in Java
Multithreading in java
Annotations in Java
Reflection in Java
Reflection & Annotations - The Powerful Combination
Run terminal commands from Java
Lambda in Java
Unit Testing in Java
Big O Notation for coding interviews
Top Java coding interview questions for SDET
